
The Codomain is actually part of the definition of the function.Īnd The Range is the set of values that actually do come out. The Codomain is the set of values that could possibly come out.
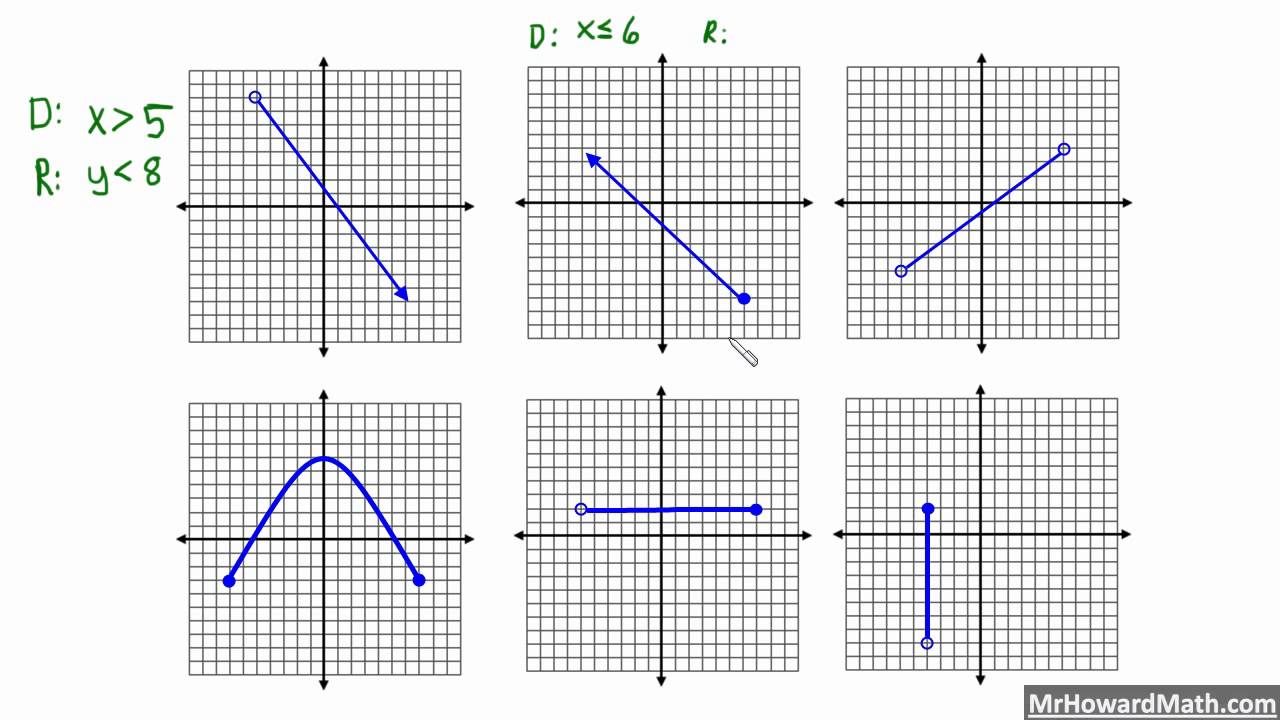
The Codomain and Range are both on the output side, but are subtly different. Or if we are studying whole numbers, the domain is assumed to be whole numbers.īut in more advanced work we need to be more careful! Codomain vs Range.Usually it is assumed to be something like "all numbers that will work".Yes, but in simpler mathematics we never notice this, because the domain is assumed: So, the domain is an essential part of the function. Range 0, Write down the interval for the principle value branch of each of the following functions and draw its graph : The value of. In this case the range of g(x) also includes 0.Īlso they will have different properties.įor example f(x) always gives a unique answer, but g(x) can give the same answer with two different inputs (such as g(-2)=4, and also g(2)=4) I like how they took the stickie strategy and made it more practical based on the writing tools they *will* have when taking the Algebra 1 EOC next week.Example: a simple function like f(x) = x 2 can have the domain (what goes in) of just the counting numbers Įven though both functions take the input and square it, they have a different set of inputs, and so give a different set of outputs. Another way to identify the domain and range of functions is by using graphs. Here are several work samples from students today showing their different interpretations of the strategy. Since I’m guessing most of my students won’t walk into the EOC with Post-Its in their pockets, I like using highlighters to color-code things a bit. If youre seeing this message, it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website. If the graph is a function state whether it is discrete continuous or neither. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Graph Convolutional Networks (UDA-GCN) for cross- domain node classication by jointly modeling local and global consistency relations of each graph, domain information, source domain information and target domain information as a unied learning framework. In the above graph: The graph encompasses all -values from to. Given the graph of a function, determine its domain or range. The domain values are at regular intervals, and the range values have a common factor of 4. I like the strategy a lot – it’s tough for kids to visualize domain and range with the plethora of unusual and squiggly graphs out there. Here’s an example of a graph, and we’ll use it to determine the domain and range. The data in the table displays exponential behavior.
#DOMAIN GRAPH HOW TO#
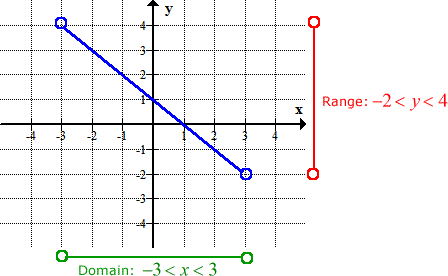
We will also review how to find the domain and range. Here, we will look at a summary of the domain and range of a function. The range can be calculated by finding the set of all possible values for the dependent variable, generally y. Now, students can see that the domain can be expressed as -5 ≤ x < 5 and the range can be expressed as 0 ≤ y < 6 (It’s easier to see on a graph whose axes are numbered a little better, but you get the idea if you peek at the original graph above). The domain can be calculated by finding the set of all possible values for the independent variable, usually x. Likewise, slide a stickie from right to left, top to bottom, and bottom to top, until the graph is framed, like so: Slide a stickie note from left to right until you “bump into” the function, and stick it on the paper. The idea is to use 4 notes so that all you see is the graph, which can make identifying the domain and range a little easier. I learned a nifty domain and range trick from an online workshop about using stickie notes to help “frame” the graph of a function.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
